Thursday, October 27, 2022
1...
min
Hydrogen can provide energy to different sectors, such as transportation, industry, buildings, and homes. It is classified by color, although not naturally, as it is colorless. There are many colors, but the most common are green, gray, and blue. Let's learn a little more about hydrogen:
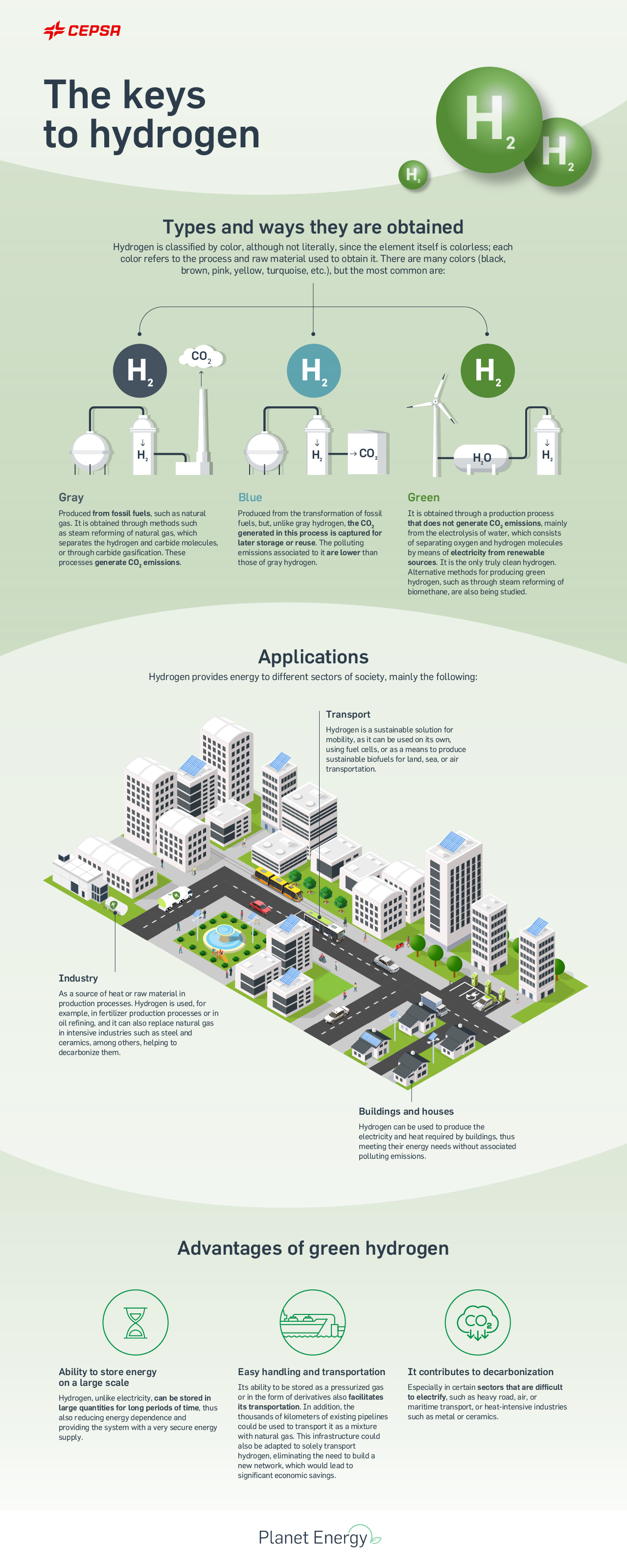
The keys to hydrogen
Types and the ways they are obtained
Hydrogen is classified by color, although not literally, since the element itself is colorless; each color refers to the process and raw material used to obtain it. The most common types are:Gray hydrogen
Produced from fossil fuels such as natural gas.Blue hydrogen
Produced by transforming fossil fuels, but the CO2 generated during the process is captured for reuse.Green hydrogen
No CO2 emissions are generated during the production process. It is the only truly clean hydrogen.Applications:
Transportation:
Hydrogen is a sustainable solution for mobility as it can be used to produce biofuels for sustainable transportation.Industry:
Hydrogen is used as a source of heat or a raw material in production processes; it is used to manufacture fertilizers or refine oil.Buildings and homes:
Hydrogen can be used to produce electricity and the heat that buildings need.Advantages of green hydrogen:
- Easy management and transportation
- Large-scale energy storage capacity
- Contributes to decarbonization
¿Te ha parecido interesante?